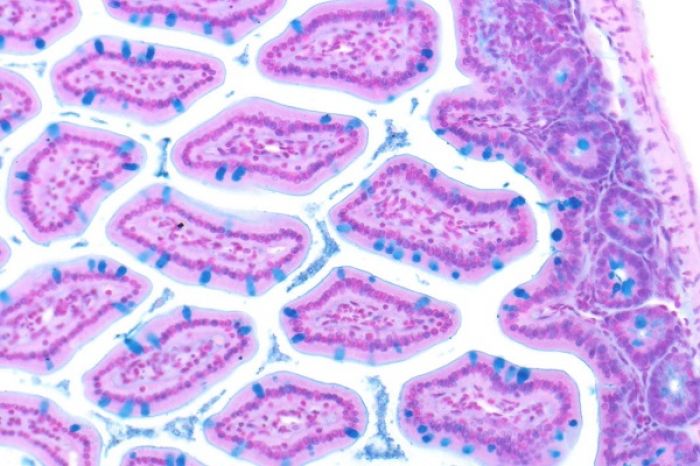
روش کار رنگ آمیزی پریودیک اسید شیف PAS
مرحله اول رنگ آمیزی PAS
ابتدا از خون حاوی ضد انعقاد گسترش تهیه می کنیم سپس صبر میک نیم تا گسترش خشک شود.
سپس لام را به مدت 10 دقیقه درون محلول تثبیت کننده قرار می دهیم.
حال لام را به مدت 10 دقیقه زیر جریان ملایم آب شستشو می دهیم.
سپس این لام را به مدت 10 دقیقه در ظرف محلول اسید پریودیک قرار می دهیم.
مجدداً لام را توسط جریان ملایم آب شستشو می دهیم و صبر می کنیم تا خشک شود.
مرحله دوم رنگ آمیزی PAS
لام را به مدت 30 دقیقه در محلول فوشین قلیایی غوطه ور کنید.
سپس لام را به مدت 3 دقیقه در محلول شستشو بالا و پایین ببرید.
حال گسترش را 5 تا 10 دقیقه زیر جریان ملایم آب شستشو دهید. سپس اجازه دهید تا لام خشک شود.
سپس رنگ هماتوکسیلین را روی لام ریخته و پس از گذشت 10 تا 15 دقیقه لام را دوباره با آب شستشو می دهیم.
پس از خشک شدن لام می توان آن را با عدسی 100 برابر زیر میکروسکوپ مشاهده کنیم.
روش تهیه محلول اسید پریودیک:
5 گرم کریستال اسید پریودیک را در 500 میلی لیتر آب مقطر حل می کنیم. این محلول را باید درون شیشه قهوه ای تیره نگهداری کنیم تا به مدت 3 ماه پایدار بماند.
روش تهیه محلول فوشین قلیایی
5 گرم فوشین را در 500 میلی لیتر آب مقطر داغ حل می کنیم. پس از خنک شدن، محلول را فیلتر می کنیم.
روش تهیه محلول تثبیت کننده
10 میلی لیتر فرمالدهید 37% را در 90 میلی لیتر اتانل خالص حل می کنیم.
روش تهیه محلول شستشو
آب مقطر حاوی گاز دی اکسید سولفور
Periodic acid–Schiff stain
Periodic acid–Schiff (PAS) is a staining method used to detect polysaccharides such as glycogen, and mucosubstances such as glycoproteins, glycolipids and mucins in tissues. The reaction of periodic acid oxidizes the vicinal diols in these sugars, usually breaking up the bond between two adjacent carbons not involved in the glycosidic linkage or ring closure in the ring of the monosaccharide units that are parts of the long polysaccharides, and creating a pair of aldehydes at the two free tips of each broken monosaccharide ring. The oxidation condition has to be sufficiently regulated so as to not oxidize the aldehydes further. These aldehydes then react with the Schiff reagent to give a purple-magenta color. A suitable basic stain is often used as a counterstain.
• PAS diastase stain (PAS-D) is PAS stain used in combination with diastase, an enzyme that breaks down glycogen.
• Alcian blue/periodic acid–Schiff (AB/PAS or AB-PAS) uses alcian blue before the PAS step.
Uses
PAS staining is mainly used for staining structures containing a high proportion of carbohydrate macromolecules (glycogen, glycoprotein, proteoglycans), typically found in e.g. connective tissues, mucus, the glycocalyx, and basal laminae.
PAS staining can be used to assist in the diagnosis of several medical conditions:
• Glycogen storage disease (versus other storage disorders).
• Adenocarcinomas, which often secrete neutral mucins.
• Paget disease of the breast.
• Alveolar soft part sarcoma.
• Staining macrophages in Whipple's disease.
• It can be used to diagnose α1-antitrypsin deficiency if periportal liver hepatocytes stain positive.
• Aggregates of PAS-positive lymphocytes are present in epidermis in Mycosis fungoides and Sezary syndrome, called Pautrier microabscesses.
• Ewing sarcoma
• Erythroleukemia, a leukemia of immature red blood cells. These cells stain a bright fuchsia.
• Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis.
• Fungal infection, the cell walls of fungi stain magenta; this only works on living fungi. In contrast, Grocott's methenamine silver stain (GMS) will stain both living and dead fungal organisms.
• It is used to identify glycogen in lung biopsy specimens of infants with pulmonary interstitial glycogenosis (PIG).
• It can be used to highlight super cross-linked lipids inclusions in ceroid lipofuscinosis (NCL).
Presence of glycogen can be confirmed on a section of tissue by using diastase to digest the glycogen from a section, then comparing a diastase digested PAS section with a normal PAS section. The diastase negative slide will show a magenta staining where glycogen is present within a section of tissue. The slide that has been treated with diastase will lack any positive PAS staining in those locations on the slide
PAS staining is also used for staining cellulose. One example would be looking for implanted medical devices composed of nonoxidized cellulose.
If the PAS stain will be performed on tissue, the recommended fixative is 10% neutral-buffered formalin or Bouin solution. For blood smears, the recommended fixative is methanol. Glutaraldehyde is not recommended because free aldehyde groups may be available to react with the Schiff reagent, which may result in false positive staining.